Nephrology at Abirami Hospital
Nephrology focuses on diagnosing, treating, and managing kidney diseases, including kidney stones and failure. Our team also provides comprehensive care for kidney-related issues associated with hypertension and diabetes.
Kidney Transplant
Our Nephrology and Urology Centers have a robust kidney transplant program, performing autologous and cadaveric transplants. We boast India's first organ transplant registry and utilize minimally invasive surgery for renal donors, reducing recovery time.
Types of Kidney Transplants
- Cadaveric renal transplantation
- Living donor kidney transplants (related and unrelated)
- Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy
What is a Kidney Transplant?
A kidney transplant involves placing a healthy kidney from a donor into a person with kidney failure. This procedure is often the best treatment for end-stage kidney disease, replacing the function of two failed kidneys with one donated kidney.
Causes of Kidney Failure
- Diabetes
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Chronic glomerulonephritis
- Polycystic kidney disease
During and After a Kidney Transplant
- Procedure: Performed under general anesthesia, with the new kidney placed in the lower abdomen. Blood vessels and the ureter are connected to the bladder.
- Post-Transplant Care: Close monitoring in the recovery area with medications to prevent rejection and manage complications. Dialysis may be needed temporarily.
Dialysis Services
- Hemodialysis: Blood is cleaned using a machine, typically three times a week, each session lasting about four hours.
Peritoneal - Dialysis: Blood is cleaned inside the body using a catheter, with options like CAPD (done manually) and APD (automated, overnight).
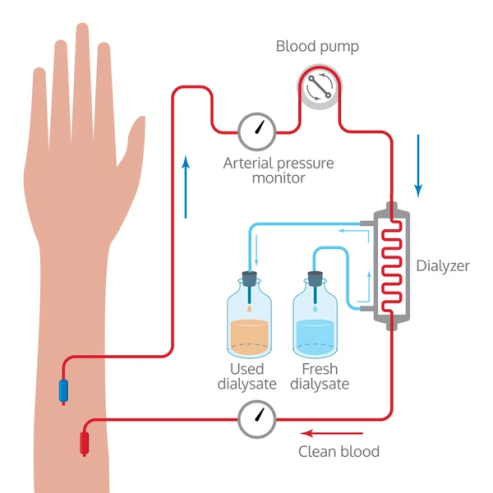
When is Dialysis Needed?
Dialysis is required when kidney function drops to less than 15%, typically in end-stage kidney failure.
Types of Dialysis
- Hemodialysis: Blood is filtered using a hemodialyser machine.
- Peritoneal Dialysis: Blood is cleaned inside the body using a catheter and dialysate.
Peritoneal Dialysis Types:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD): Done manually, typically four or five times a day.
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD): Performed using a machine, typically during the night.
Diet and Lifestyle:
Dialysis patients thrive with tailored diets and smoothly resume daily activities, including work. Our expert guidance ensures a seamless adaptation to treatment for a fulfilling life.


